
Please note that these are basic tests to see if your scale is internally reliable. For the variable Abtot, here is that output: This ensures that all of the variables in the scale are measuring the same characteristic.
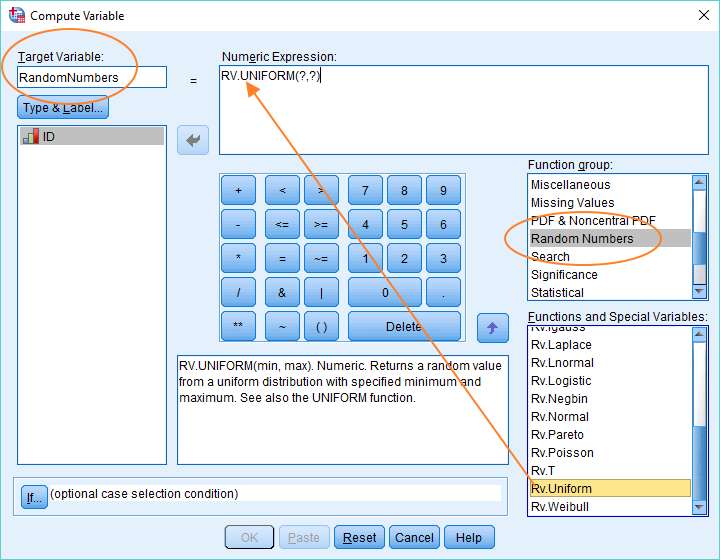
You will also want to check the Inter-Item Correlation box to ensure that all of the values are positive. 7, so this scale has relatively good internal reliability. The first part of your output will look like this:Ĭronbach’s Alpha is greater than. Type the name of your new variable into the “Scale Label Box”. Then move all of the items of your scale into the box “Items”. To check on the reliability of your scale: click Analyze, Scale, and Reliability Analysis. Be aware that the Cronbach test is highly dependent upon the number of items in the scale (especially less than 10). The most commonly used test is Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. You can assume reliability if the coefficient is greater than. Once you have created a scale, you should test to see if it is reliable that is, to see if the scale items are internally consistent. Remember to go to the Variable View and define your values of your new, recoded variable! Your new variable will be listed at the end of your variables. Your screen should look like this:Ĭlick OK. Go back and add each variable that you want included in your scale by using these steps. Highlight the first variable that you want included in your scale variable, click on the arrow and then use the “+” sign on the calculator. Enter the label that you are giving to your new variable and make sure that the “numeric” box is checked. In the field “Target Variable”, type the name of your new variable (AbTotal). Click the button “Type and Label”. In Data View, go to: Transform, Compute Variable. Once you have addressed these issues, you can create a new scale variable that combines responses to the five specific questions. not applicable = 0, “don’t know” = 8, missing = 9).
SPSS COMPUTE VARIABLE CODE
Also make sure that you mark all missing answers with the same code as well. (e.g. If you find that the questions are not the same in either coding or phrasing, go back and recode those variables so that the codings are identical. “yes” = 1, “no” = 2)? Are some questions positively worded and other negatively phrased? Sometimes question wording is reversed to ensure that people are paying attention to the question.

Do all of the variables identically code the responses (e.g. First, examine the questions that you intend to use to create your scale. You can easily construct a scale about general opinions on abortion using SPSS. Specifically, we could simply add the number of Yes answers across the seven questions for a sum for each study participant of 0 to 7.There may be times when you wish to combine several variables that focus upon a related topic into a scale.įor example, the 2008 General Social asks specific “yes/no” variables regarding opinions on abortion under the following circumstances: defect of the baby (Abdefect), health of the mother (Abhealth), rape (Abrape), when a married woman wants no more children (abnomore), and because a woman is single (Absingle). While the individual questions are useful for gaining a sense of the participant's views on whether or not abortion should be legal in specific cases, by combining the variables it is possible to get a better overall measure of opinion on abortion permissiblity. E.g., Do you think a woman should be allowed to obtain an abortion if she has been raped? If she doesn't want any more children? Et cetera. Participants were asked a set of seven questions to learn in what circumstances s/he believed abortion should be allowed. In our Genetic Counselors study, a subject investigated was attitude towards (an unpleasant operation, my apologies) abortion. One common reasons is creation of a scale measure that combines several existing variables into a single variable, such as to summarize a phenomenon of interest. Computing variables in SPSS refers to computing with existing variables to create new variables.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
